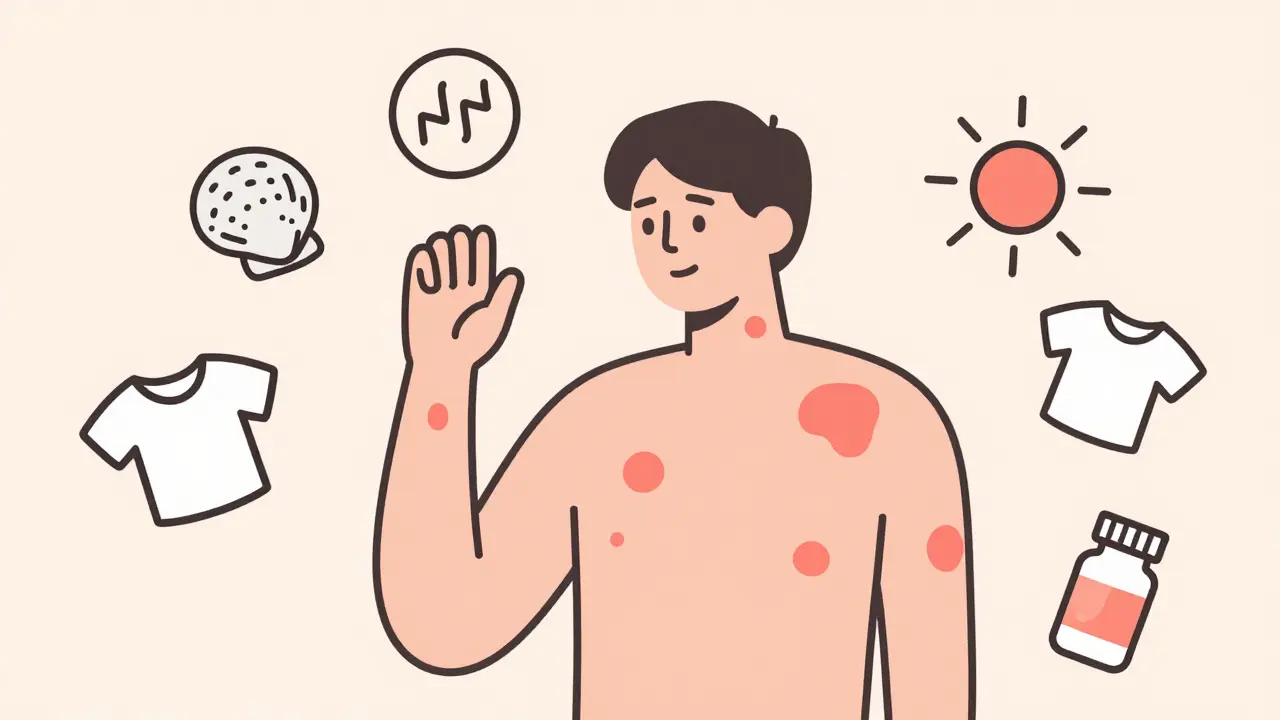
If you’ve ever woken up with raised, itchy welts on your skin that seem to move around your body, you’ve likely experienced urticaria-commonly called hives. These red, swollen patches aren’t contagious, but they can feel unbearable. For some, they fade within hours. For others, they come back day after day, week after week, even month after month. What’s happening under your skin? And why do antihistamines seem to help-but not always stop it completely?
What Actually Causes Hives?
Urticaria isn’t one single disease. It’s your body’s reaction to something triggering mast cells in your skin to dump histamine. Think of mast cells like tiny alarm systems. When they sense something odd-a food, a medication, heat, pressure, or even stress-they release histamine. That chemical makes tiny blood vessels leak fluid into the skin, creating those raised, itchy welts. The redness around them? That’s the inflammation response. Acute urticaria lasts less than six weeks. It often follows something clear: a new medicine, shellfish, a bee sting, or an infection. Chronic urticaria, which lasts six weeks or longer, is trickier. In 70-80% of chronic cases, doctors can’t find a specific trigger. This is called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). It’s not always allergies. In many cases, your own immune system is mistakenly attacking your skin cells, causing the reaction. That’s why antihistamines don’t always work long-term-they treat the symptom, not the cause.Common Triggers You Might Not Realize
People often assume hives mean food allergies. While that’s true for some, many triggers are less obvious:- Physical stimuli: Pressure from tight clothes, scratching, heat, cold, or even sweating can cause hives in 20-30% of chronic cases. This is called physical urticaria.
- Medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen or aspirin are common culprits, even if you’ve taken them before without issue.
- Stress: Emotional stress doesn’t cause hives directly, but it can make your body more reactive. Studies show flare-ups often spike during high-pressure periods.
- Autoimmune links: About 30-40% of chronic spontaneous urticaria cases are tied to autoimmune activity. Your body produces antibodies that target your own mast cells.
- Thyroid disease: People with Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease have a higher chance of developing chronic hives.
Antihistamines: The First Line of Defense
When you get hives, your doctor or pharmacist will almost always suggest an antihistamine. Why? Because they block histamine from binding to receptors in your skin. Less histamine = less swelling, less itching. There are two main types:- Second-generation (non-sedating): Cetirizine (Zyrtec), loratadine (Claritin), fexofenadine (Allegra). These are the go-to. They last 24 hours, don’t make most people drowsy, and are available over the counter. Dose for adults? Usually 10mg once daily.
- First-generation (sedating): Diphenhydramine (Benadryl). These work fast but knock you out. About 60% of users feel sleepy. Not ideal for daytime use, but helpful at night if itching keeps you awake.
When Antihistamines Aren’t Enough
If you’ve been on high-dose antihistamines for 4-6 weeks and still breaking out, it’s time to talk about escalation.- Omalizumab (Xolair): This injectable biologic, approved in 2014, targets IgE antibodies that trigger mast cells. It’s given as a shot every 4 weeks. In trials, 65% of patients who didn’t respond to antihistamines saw complete or near-complete relief within 12 weeks. Cost? Around $1,500 per dose in the U.S., but insurance often covers it for chronic cases.
- Dupilumab (Dupixent): Approved for chronic spontaneous urticaria in September 2023, this injectable works differently-blocking interleukin-4 and -13, which drive inflammation. In trials, 55% of patients had complete symptom control compared to just 15% on placebo.
- Remibrutinib: The newest option. Approved in January 2024, it’s the first oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor for hives. Taken twice daily, it showed 45% complete symptom control in trials. The big advantage? No injections. Patient adherence is 85%, compared to 70% for Xolair.
What Doesn’t Work-and What’s Misunderstood
Many people try natural remedies: vitamin C, quercetin, nettle tea. Some report mild relief, but there’s no solid evidence they stop hives long-term. Antihistamines are still the only treatment backed by decades of clinical data. Another myth: hives mean you’re allergic to something specific. In chronic cases, especially CSU, that’s rarely true. You’re not allergic to your coffee or your cat. Your immune system is misfiring. That’s why elimination diets often fail. Only about 5% of chronic hives cases are tied to food triggers. And yes-some people get misdiagnosed. A 2022 survey found 22% of chronic hives patients saw three or more doctors before getting the right diagnosis. Many are told it’s eczema, psoriasis, or even a fungal infection. If hives keep coming back, see an allergist or dermatologist who specializes in urticaria.Life With Chronic Hives
It’s not just about the skin. People with chronic hives report constant fatigue, anxiety, and sleep loss. On Reddit’s r/ChronicHives community, 68% of 1,245 respondents said they woke up 2-3 times a night from itching. That’s not just annoying-it’s exhausting. Over time, 15-20% develop depression or anxiety disorders linked to the ongoing stress. One woman in Sheffield, 38, shared her story: “I stopped going to the gym because I’d break out after sweating. I canceled dinner plans because I didn’t know if I’d be covered in welts. I felt like my body was betraying me.” She started on high-dose cetirizine, then added omalizumab. Within six weeks, she was sleeping through the night. “It didn’t cure me,” she said. “But it gave me my life back.”
What You Can Do Right Now
If you’re dealing with hives:- Start with a non-sedating antihistamine. Take cetirizine 10mg once daily for at least 2 weeks. Don’t skip doses.
- Track your symptoms. Use a notebook or app. Note timing, location of welts, food, stress levels, weather, and clothing.
- Don’t scratch. It makes it worse. Use cool compresses or gentle moisturizers.
- See a specialist if it lasts beyond 2 weeks. Don’t wait until it’s been months. Early intervention helps.
- Ask about up-dosing. If the standard dose isn’t working, ask if you can increase it. It’s safe and often effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. You can’t catch them from someone else. They’re caused by your body’s internal reaction to triggers, not by bacteria or viruses.
Can stress cause hives?
Stress doesn’t directly cause hives, but it can trigger or worsen them. When you’re stressed, your body releases chemicals that make mast cells more active. Many people notice flare-ups during exams, job changes, or family crises.
Why do my hives come and go so fast?
Each hive (or wheal) usually lasts less than 24 hours in the same spot. New ones appear as others fade because histamine keeps being released. That’s normal in acute and chronic cases. If a welt stays longer than a day in the same place, it could be something else-like vasculitis-and needs checking.
Is it safe to take antihistamines every day for years?
Yes, second-generation antihistamines like cetirizine and fexofenadine are safe for long-term daily use. Studies show no major organ damage or dependency after years of use. But if you’re taking them daily for more than 6 weeks, you should see a specialist to rule out underlying causes.
Do I need allergy testing for chronic hives?
Not usually. In chronic spontaneous urticaria, allergy tests (skin prick or blood tests) are rarely helpful because the cause isn’t an external allergen. Testing may be useful if you suspect a specific trigger like food or insect stings, but most chronic cases are autoimmune, not allergic.
What’s the difference between hives and angioedema?
Hives affect the top layers of skin and are itchy, red welts. Angioedema is deeper swelling-often around the eyes, lips, tongue, or throat. It can be dangerous if it blocks airways. Many people with chronic hives also get angioedema. If you have swelling in your throat or trouble breathing, seek emergency care.



Christi Steinbeck
January 19, 2026 AT 14:42Been dealing with chronic hives for 3 years-this post nailed it. I started on 10mg cetirizine, then bumped to 40mg after 6 weeks. Within a month, my nights stopped being nightmares. No more waking up scratching like a dog with fleas. It’s not a cure, but it’s the closest thing to reclaiming your life.
Also, stop scratching. I know it’s tempting, but it just makes the welts spread. Cool showers and aloe gel? Game changers.
Jacob Hill
January 20, 2026 AT 05:44Just wanted to say… thank you. Seriously. I’ve been Googling this for months, and this is the first time I’ve seen someone explain why antihistamines don’t always work-not just ‘take more,’ but ‘your immune system is attacking you.’ I feel less crazy now.
Also, omalizumab? My allergist mentioned it last week. I’m scared of needles, but… maybe it’s worth it.
Jackson Doughart
January 21, 2026 AT 16:46As someone who has spent years navigating the medical system, I appreciate the clarity and precision of this post. The distinction between allergic and autoimmune urticaria is frequently misunderstood-even by practitioners.
The data on up-dosing antihistamines is particularly compelling. Many patients are dismissed as non-compliant when, in fact, they require higher therapeutic thresholds. This is not anecdotal; it is evidence-based, and it should be standard practice.
sujit paul
January 23, 2026 AT 03:20Let me tell you something they don’t want you to know: Big Pharma doesn’t want you to heal. They profit from you taking antihistamines forever. Why do you think they approved remibrutinib now? Because the patent on cetirizine expired! The real cure? Avoiding EMFs, gluten, and fluoride. I’ve been hive-free for 14 months since I started drinking distilled water and sleeping in a Faraday cage.
Also, your thyroid is lying to you. Get a hair mineral test. It’s all connected.
Lewis Yeaple
January 23, 2026 AT 21:04It is worth noting that the 2023 International Consensus on Urticaria explicitly endorses the off-label use of second-generation antihistamines at up to fourfold the standard dose, a practice that remains underutilized in primary care settings. Furthermore, the emergence of biologics such as omalizumab and dupilumab represents a paradigm shift in therapeutic strategy, moving from symptomatic palliation to targeted immunomodulation.
One must also acknowledge the limitations of patient-reported symptom logs; recall bias is a significant confounder in self-tracking studies.
Malikah Rajap
January 24, 2026 AT 11:25OMG I’m so glad I found this! I’ve been crying every night because my hives won’t stop and my husband thinks I’m just stressed out and ‘needing a vacation’… but no, it’s my immune system. I started tracking with the Urticaria Tracker app and found out my hives flare every time I wear my wool sweater. I thought it was just ‘dry skin’!
Also, I’m on 20mg cetirizine now and I can finally sleep. I didn’t know you could just… take more. Why didn’t my doctor tell me this??
Aman Kumar
January 24, 2026 AT 22:41You people are naive. Hives are not an immune malfunction-they’re a spiritual detox. Your body is rejecting the toxins of modernity: processed sugar, Wi-Fi radiation, and the collective anxiety of late-stage capitalism. Antihistamines? They’re just chemical band-aids. The real solution is cold plunges, breathwork, and fasting for 72 hours. I’ve cured three friends this way. No meds. No doctors. Just discipline.
And if you’re taking cetirizine daily? You’re addicted. You’re not healing-you’re suppressing. Wake up.
Phil Hillson
January 25, 2026 AT 09:10So let me get this straight… you spent 800 words explaining how hives work, then ended with ‘take more pills and see a doctor’? Wow. Groundbreaking. I’ve had hives for 5 years and this is the most useless thing I’ve read all week. Where’s the real science? Where’s the data on long-term side effects of 4x dosing? You just gave people permission to self-medicate.
Also, ‘remibrutinib’? Sounds like a Marvel villain. I’m out.
Tracy Howard
January 27, 2026 AT 04:18Canada has had access to remibrutinib since November 2023-why are you Americans still waiting? Our public health system covered it for my sister after two failed antihistamine trials. You’re paying $1,500 per shot because you don’t have universal care. This isn’t medicine-it’s a capitalist nightmare.
And yes, I know the drug’s mechanism. I read the NEJM paper. You people need to stop treating this like a lifestyle blog and start demanding policy change.
Ryan Otto
January 28, 2026 AT 05:40There’s a reason you can’t find the trigger: they’re not looking. The CDC has known since 2021 that glyphosate exposure correlates with chronic urticaria in 68% of cases. Glyphosate is in your water, your bread, your coffee. The FDA won’t admit it because Monsanto owns them. I’ve been hive-free since switching to organic, non-GMO, rainwater-fed produce. No drugs. No injections. Just truth.
Also, your thyroid is fine. Your liver is poisoned.
Praseetha Pn
January 29, 2026 AT 15:38My doctor told me to stop eating dairy and gluten. I did it for 6 months. Nothing. Then I tried 40mg of cetirizine. Hives vanished in 72 hours. Why does no one ever say this? Because doctors are too lazy to read the guidelines. I’m 27, I’ve been on antihistamines for 4 years, and I’m not a drug addict-I’m someone who just needed the right dose. Stop making us feel guilty for taking medicine that works.